Public perception of the risks associated with antimicrobial resistance (AMR)
Published:
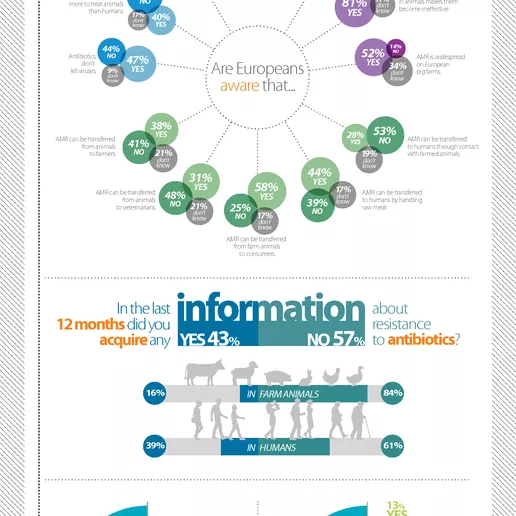
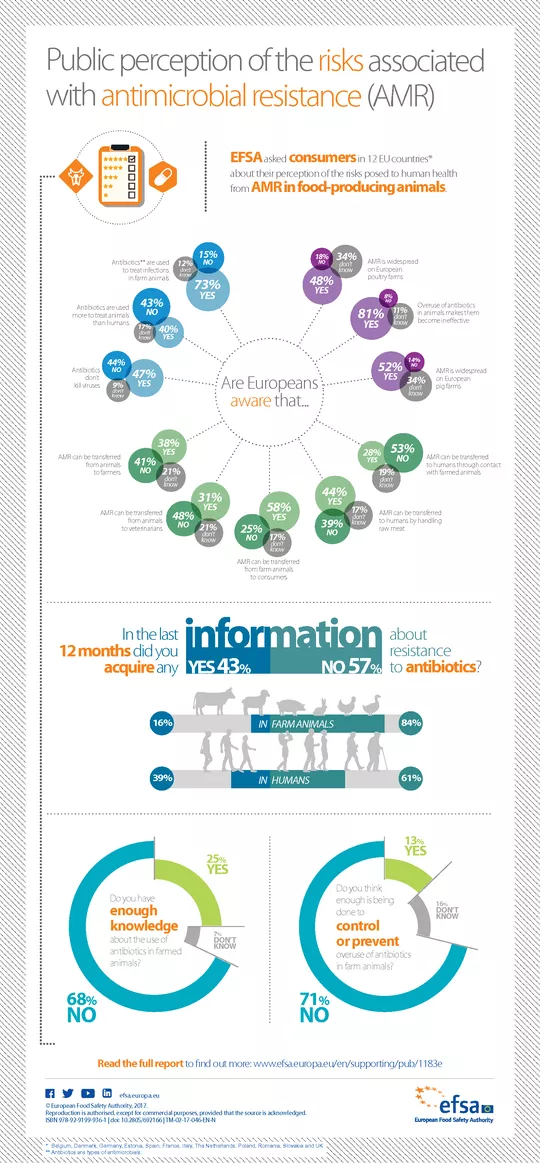
EFSA asked consumers in 12 EU countries (Belgium, Denmark, Germany, Estonia, Spain, France, Italy, The Netherlands, Poland, Romania, Slovenia and UK) about their perception of the risks posed to human health from AMR in food-producing animals.
Are Europeans aware that...
| Are Europeans aware that... | Yes | No | Don't know |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMR is widespread on European poultry farms | 48% | 18% | 34% |
| Overuse of antibiotics in animals makes them become ineffective | 81% | 8% | 11% |
| AMR is widespread on European pig farms | 52% | 14% | 34% |
| AMR can be transferred to humans through contact with farmed animals | 28% | 53% | 19% |
| AMR can be transferred to humans by handling raw meat | 44% | 39% | 17% |
| AMR can be transferred from farm animals to consumers | 58% | 25% | 17% |
| AMR can be transferred from animals to veterinarians | 31% | 48% | 21% |
| AMR can be transferred from animals to farmers | 38% | 41% | 21% |
| Antibiotics don’t kill viruses | 47% | 44% | 9% |
| Antibiotics are used more to treat animals than humans | 40% | 43% | 17% |
| Antibiotics* are used to treat infections in farm animals | 73% | 15% | 12% |
*Antibiotics are types of antimicrobials
In the last 12 months did you acquire any information about resistance to antibiotics?
- In farm animals: 16% yes, 84% no
- In humans: 39% yes, 61% no
Do you have enough knowledge about the use of antibiotics in farmed animals?
- 25% yes
- 68% no
- 7% don't know
Do you think enough is being done to control or prevent overuse of antibiotics in farm animals?
- 13% yes
- 71% no
- 16% don't know
Read the full report to find out more.